Pipeline
Current Pipeline
The following list contains our most current pipeline of completed preclinical work and
ARDScells Phase 3
Phase IIb/III Trial of Umbilical Cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
(IIb/III UC-MSCs for ARDS)
REDUCTION OF NEUTROPHIL EXTRACELLULAR TRAP FORMATION BY MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS AND THEIR EXOSOMES
Publication number: 20230107484
Abstract: Disclosed are methods of reducing lung inflammation in acute respiratory distress syndrome elicited by various factors such as COVID-19 infection by reduction of neutrophil extracellular trap formation through administration of mesenchymal stem cells and/or exosomes thereof. The invention provides means of inhibiting neutrophil release of extracellular traps by mesenchymal stem cells and/or exosomes derived from said mesenchymal stem cells. Additionally, synergies are provided between mesenchymal stem cells and/or exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells and agents approaches which reduce neutrophil extracellular trap formation.
JadiCell ARDS Phase 3
Umbilical Cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Patients with COVID-19 (“UC-MSC for COVID-19”) IND # 19757
The primary objective will be to assess effectiveness of UC-MSC treatment on proportion of patients alive and free of respiratory failure at Day 60 after randomization. The secondary objectives will be to assess all-cause mortality at Day 60, survival at day 31, number of subjects experiencing serious adverse events (SAEs) by day 31, SAE-free survival, time to recovery (evaluated until day 60), and time to oxygen requirement equal or below 40% oxygen.
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR THE CLINICAL DERIVATION OF AN ALLOGENIC CELL AND THERAPEUTIC USES
US 9,803,176 B2
Abstract: Various cells, stem cells, and stem cell components, including associated methods of generating and using such cells are provided. In one aspect, for example, an isolated cell that is capable of self-renewal and culture expansion
CTEcells Phase 1/2
Investigation of Umbilical Cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Patients IND # 27377
To determine safety and efficacy of 100 million intravenously administered CTEcells™ allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Efficacy will be determined by behavioral scores, brain imaging, and reduction in inflammatory markers. Toxicity of treatment was evaluated for the duration of the study and will be graded according to the criteria of the World Health Organization.
PROTECTION AND REGENERATION OF NEUROLOGICAL FUNCTION BY USING STEM CELLS
Publication number: 20220125852
Abstract: Disclosed are therapeutic compounds, protocols, and compositions of matter useful for treatment of neurological conditions. In one embodiment the invention teaches the treatment of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) through protecting/regenerating the endothelial by administration of cells such as stem cells. In one embodiment stem cells are administered in order to protect the endothelium from apoptosis and to preserve the blood brain barrier. In another embodiment stem cells are administered together with endothelial progenitor cells in order to regenerate neural endothelium. In other embodiments preservation of brain integrity in conditions of degeneration is accomplished by administration of stem cells and/or endothelial cells.
JadiCell COPD Phase 1/2
JadiCell Therapy for COPD IND # 28508
To determine safety and efficacy of intravenously administered allogeneic JadiCell umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD. The Primary Endpoint, which is toxicity, will be assessed by number of adverse events (AEs). The Secondary Endpoint, which is efficacy will be evaluated at baseline and days 30, 60, and 90.
UMBILICAL CORD MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE AND LUNG DEGENERATION
Publication number: 20230057957
Abstract: The invention discloses means of treating lung degenerative diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CODP) using umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells such as JadiCells alone, and/or using said cells under conditions that are activated in order to endow enhanced regenerative activity. In one embodiment said activation of said mesenchymal stem cells is performed through stimulation with a toll like receptor agonist at a concentration and duration sufficient to induce a >50% increase in keratinocyte growth factor expression from said stem cells. In another embodiment the invention provides the use of JadiCells as a means of producing exosomes, wherein said exosomes possess therapeutic properties capable of reducing inflammation, fibrosis and degeneration associated with COPD, as well as stimulation of regenerative activity. In some JadiCells are activated by a treatment with Activated Protein C.
StemVacs-A Phase 1
Safety, Feasibility, and Immunomodulatory Activities of StemVacs in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors IND # 17448
The Primary Objective is safety and feasibility of StemVacs administration at 12 months as assessed by lack of adverse medical events. The Secondary Objective is efficacy as judged by tumor response, time to progression, and immunological monitoring.
Stimulation of Immunity to Tumor Stem Cell Specific Proteins by Peptide Immunization
Application Number: 62/478532
Abstract: Treatment of cancer is disclosed through administration of proteins or specific peptides found on tumor stem cells in vivo, in a matter eliciting monocyte or dendritic cell migration in order to allow uptake of said administrated proteins or peptides, followed by administration of a maturation signal in vivo. The invention provides for treatment of cancer through induction of anticancer immunity and/or immunity towards tumor initiating stem cells.
StemVacs-V Phase 1/2
Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer by StemVacs-V Cancer Immunotherapeutic IND transferred to Res Nova Bio,Inc.
The Primary Objective is safety and feasibility of StemVacs-V administration at 12 months as assessed by lack of adverse medical events. The Secondary Objective is efficacy as judged by tumor response, time to progression, and immunological monitoring.
Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Dendritic Cells and Engineered Dendritic Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy
Publication number: 20220298491
Abstract: Disclosed are populations of dendritic cells generated from stem cells capable of inducing immunity towards cancer. In one embodiment said dendritic cells are generated from allogeneic inducible pluripotent stem cells, for some uses, said pluripotent stem cells are genetically engineered/edited to induce cancer specific immunity and/or resist immunosuppressive effect of tumor derived microenvironment. In one embodiment pluripotent stem cells are transfected with cancer stem cell antigens such as BORIS and/or NR2F6.
EpilepCells (Epilepsy) [Preclinical Done]
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy of Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
Application No.: 63418861
Disclosed are novel compositions of matter and treatment methods for reducing and/or reversing epilepsy through administration of mesenchymal stem cells in order to induce immune modulation and/or regenerative processes. In one embodiment umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are administered to a patient suffering from epilepsy at a concentration and frequency sufficient to inhibit neuronal hyperactivation and/or reduce neuroinflammatory status of the patient.
ALScells [Preclinical Done]
Protection and Regeneration of Neurological Function by Using Stem Cells
Publication number: 20220125852
Abstract: Disclosed
Examples
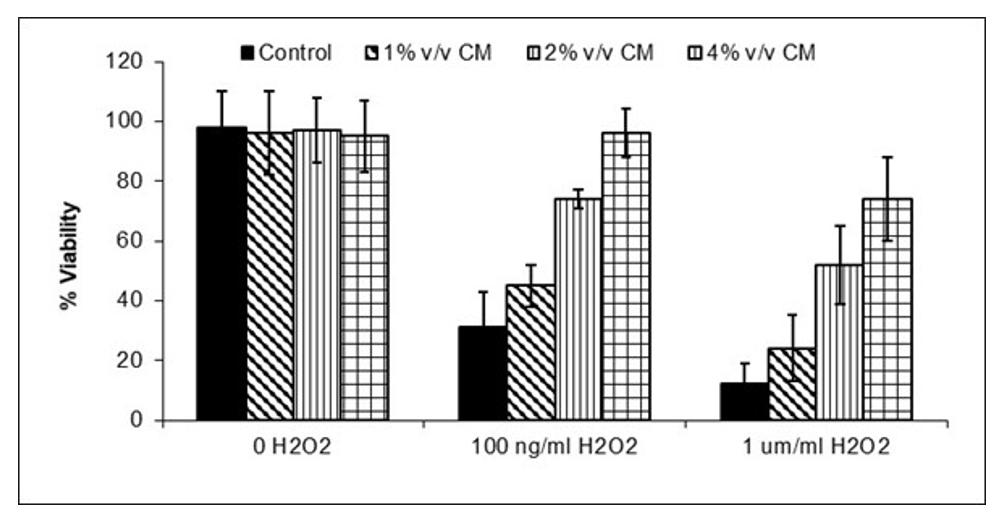
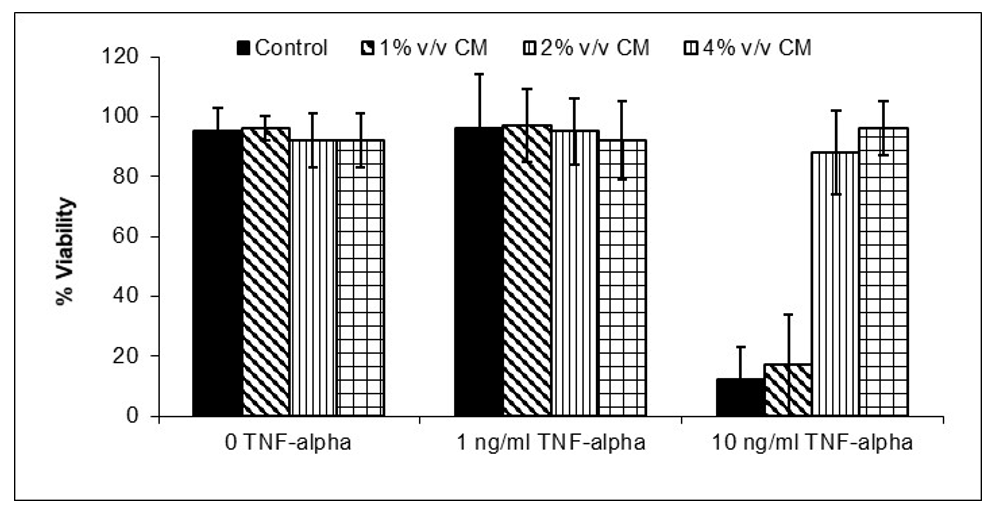
JadiCell Conditioned Media Inhibits Endothelial Death.
Injury associated with inflammation. Inflammation causes oxidative stress. Oxidative stress induces
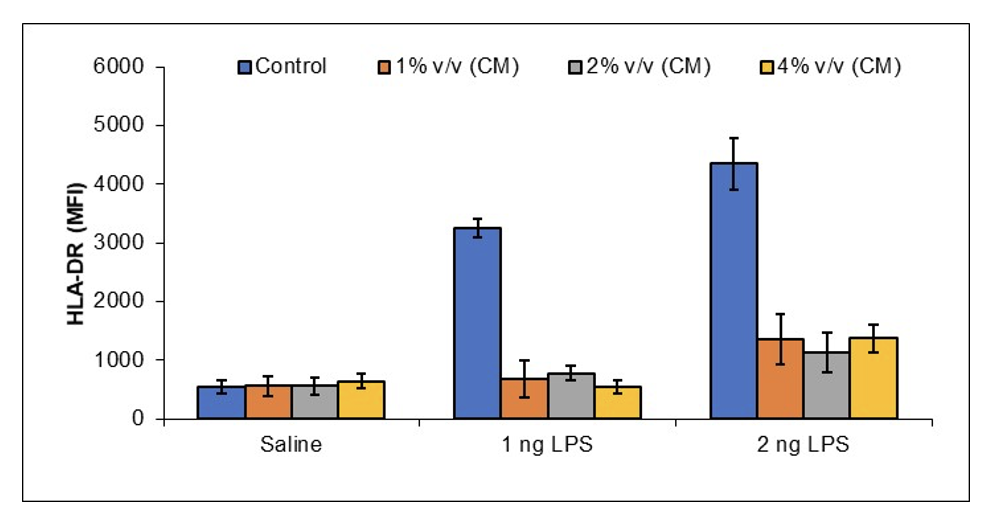
JadiCell™ Reduces Immunogenicity of Endothelial Cells
Endothelial cells can act as
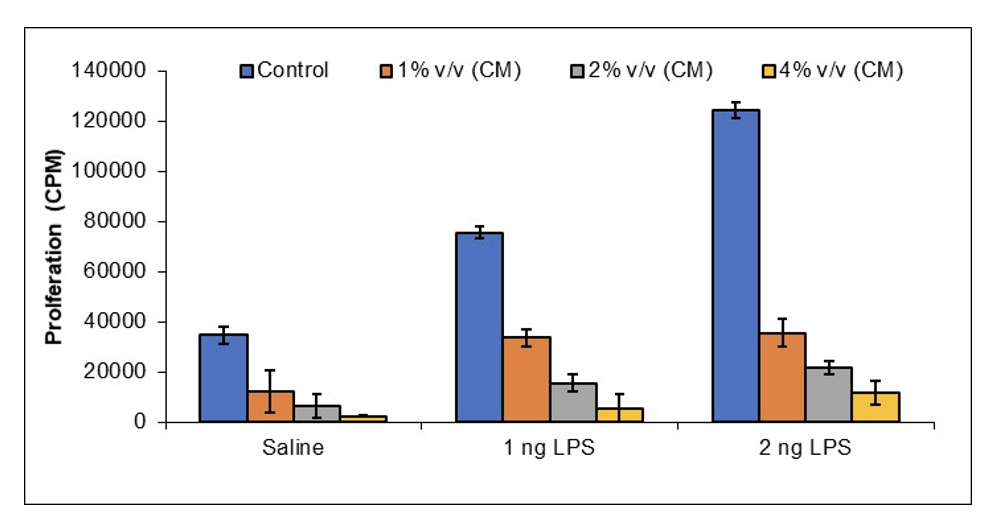
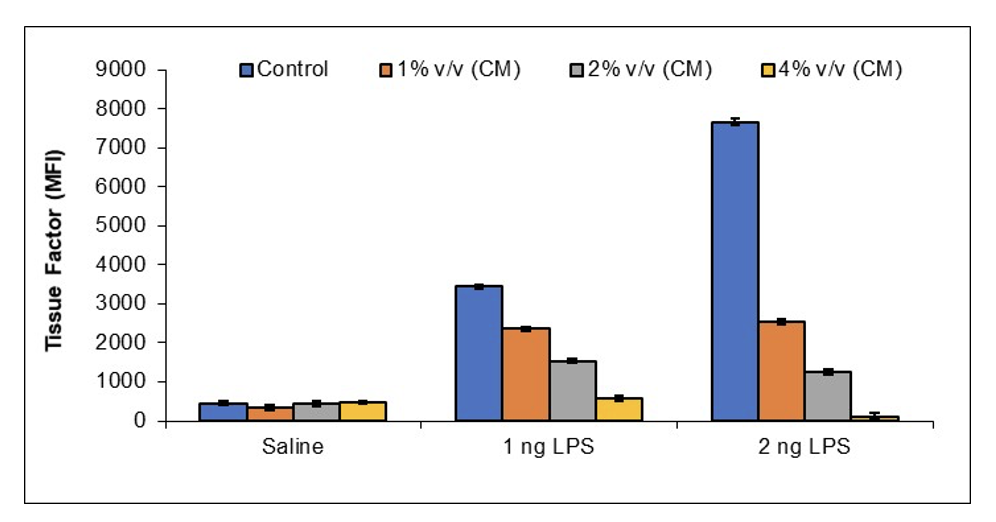
JadiCell™ Reduces Thrombogenicity of Activated Endothelial Cells
In response to
StemVacs-E [Preclinical Done]
Chimeric Cells Comprising Dendritic Cells and Endothelial Cells Resembling Tumor Endothelium
Publication number: 20220306994
Abstract: Disclosed
Example
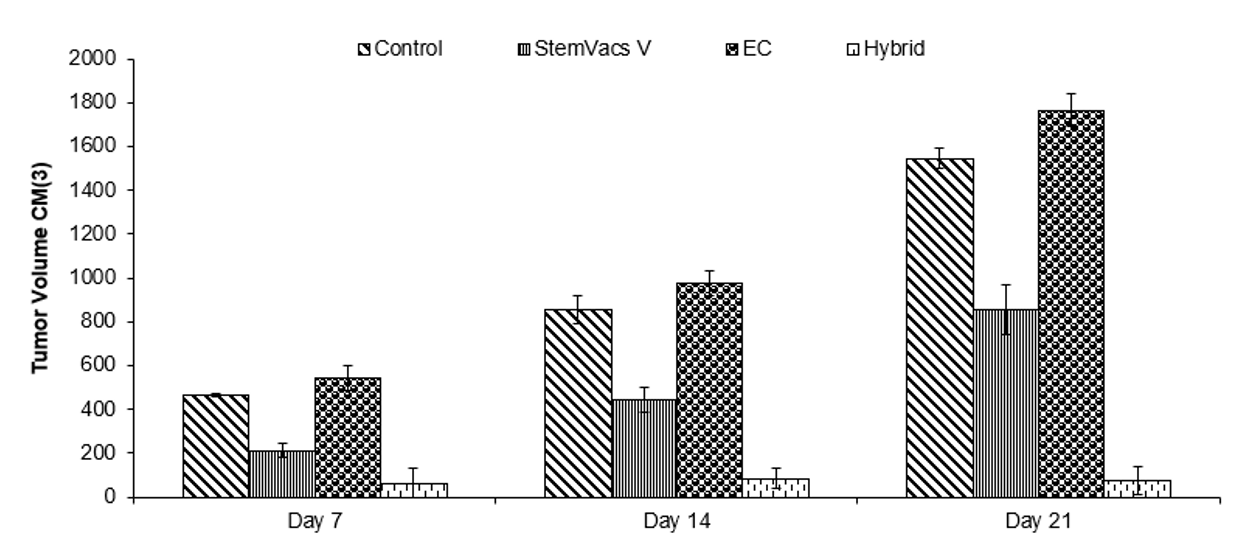
iPSCs (ATCC-DYR0100 Human Induced Pluripotent Stem (IPS) Cells (ATCC® ACS-1011™) were cultured on feeder layers of OP9 cells for 6 to 7 days in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FBS. The mesodermally differentiated cells were then harvested, reseeded onto fresh OP9 cell layers, and cultured in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FBS, 20 ng/mL GM-CSF, and 50 μmol/L 2-ME. On
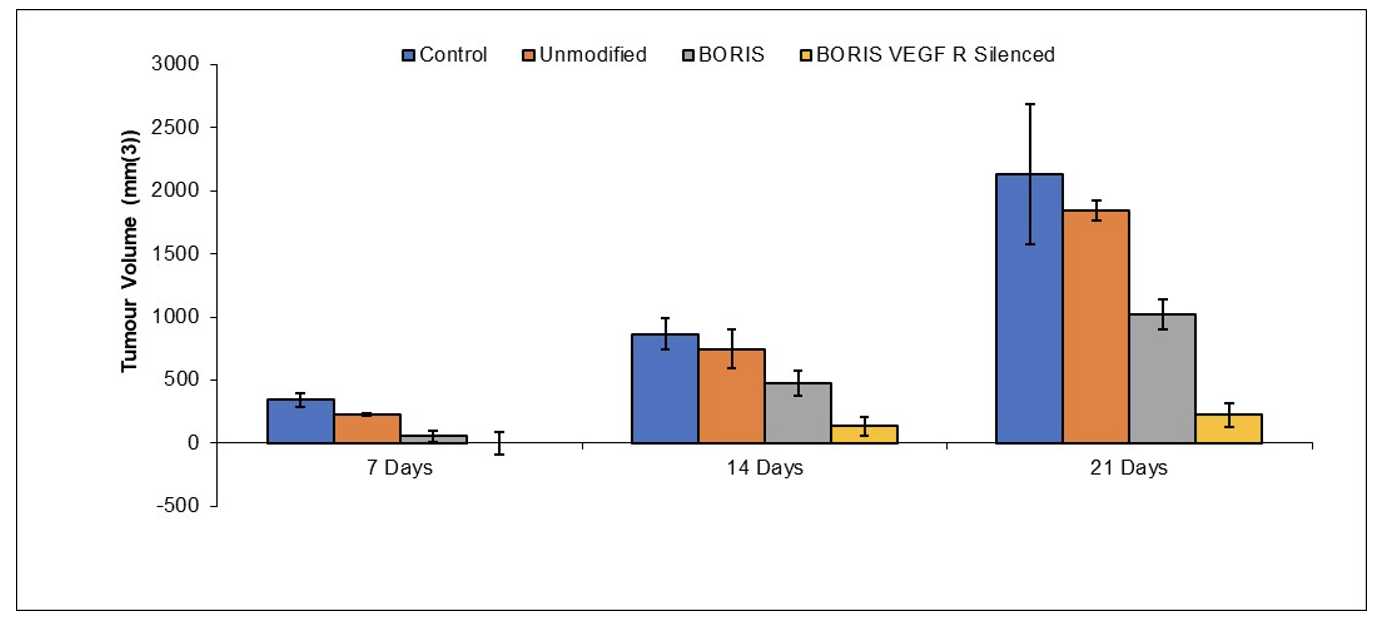
Mice were inoculated with 500,000 lewis lung carcinoma cells. Mice were injected with saline (Control), BORIS expressing VEGF R silenced dendritic cells (StemVacs-V),
StemVacs-P [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease by Immune Modulation and Regenerative Means
Application No.: 63/218,582
Disclosed are means, methods and compositions of matter for treatment Parkinson’s Disease through concurrent immune modulation and regenerative means. In one embodiment Parkinson’s Disease is treated by augmentation of T regulatory cell numbers and/or activity while concurrently providing regenerative cells such as mesenchymal stem cells, and/or dopamine secreting cells. In one embodiment administration of immunoglobulins such as IVIG together with low dose interleukin-2 and/or low dose naltrexone is disclosed as a preparatory means prior to administration of therapeutic cells such as stem cells. Other therapeutic means utilized in an adjuvant manner are also provided for hormonal rebalancing, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and deep brain stimulation.
StemVacs-C [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with Dendritic Cells for Innate and/or Adaptive Immunity
Publication number: 20210393681
Abstract: Disclosed
Examples
Materials and Methods
Cell Lines
HeLa human cervical cancer cells were obtained from American Type Tissue Culture (ATCC: Manassas, VA) and grown under
PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS (PBMC)
CELL TREATMENTS AND ANALYSIS
HeLa cells were plated at a concentration of 10,000 cells per well in flat bottom plates and incubated with dilutions of
To evaluate cell survival, 20 μl of MTT solution (5 mg/ml in PBS) was added to each well and incubated for 3 h. Then gently 150 μl of old medium containing MTT was replaced by DMSO and pipetted to dissolve any formed formazan crystals. Absorbance was then determined at 540 nm by
ELISA
IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-10
Dendritic Cells
DC
Blockade of TLR-4 was performed using
Results
Figure 1:
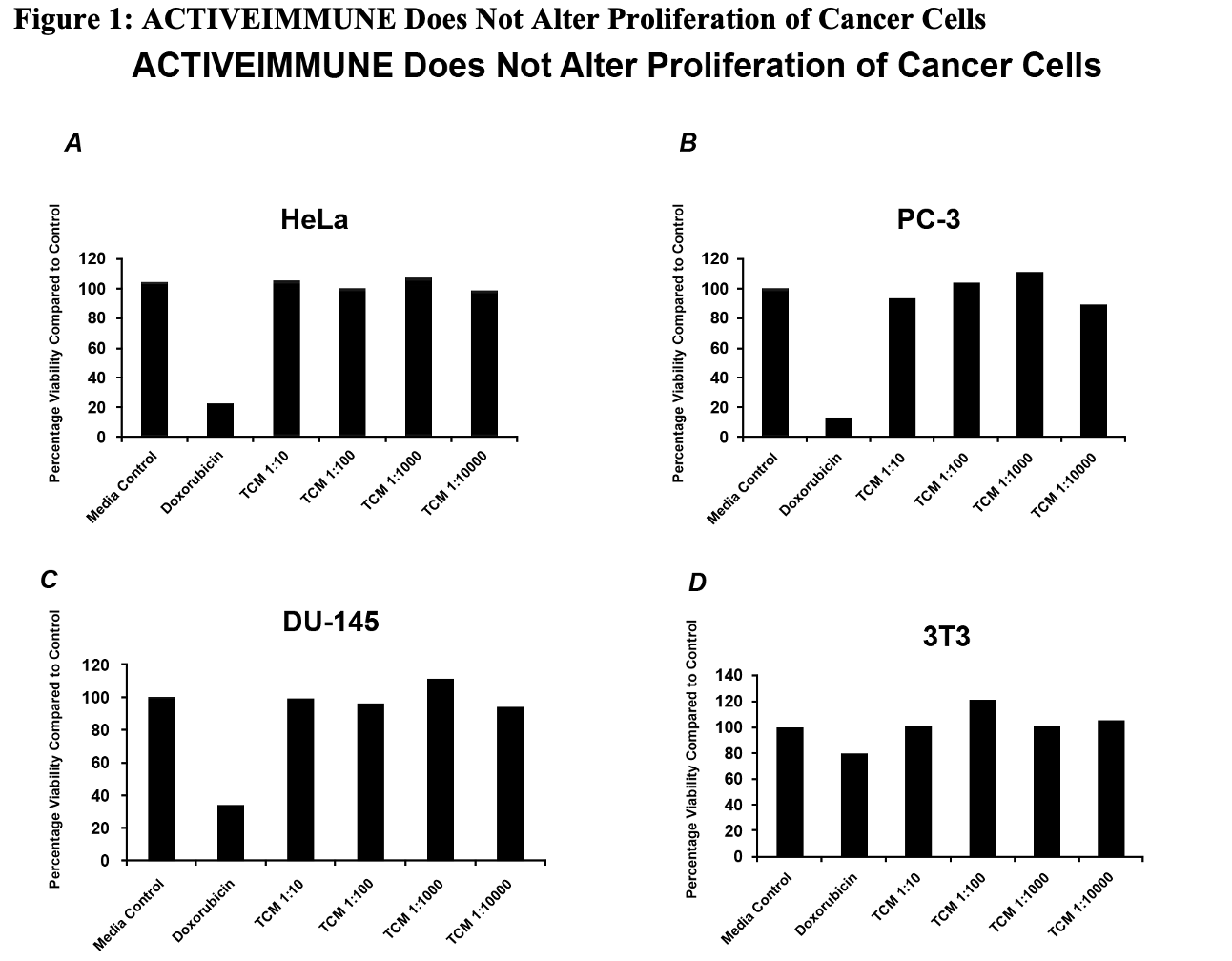
To assess whether
Figure 2:
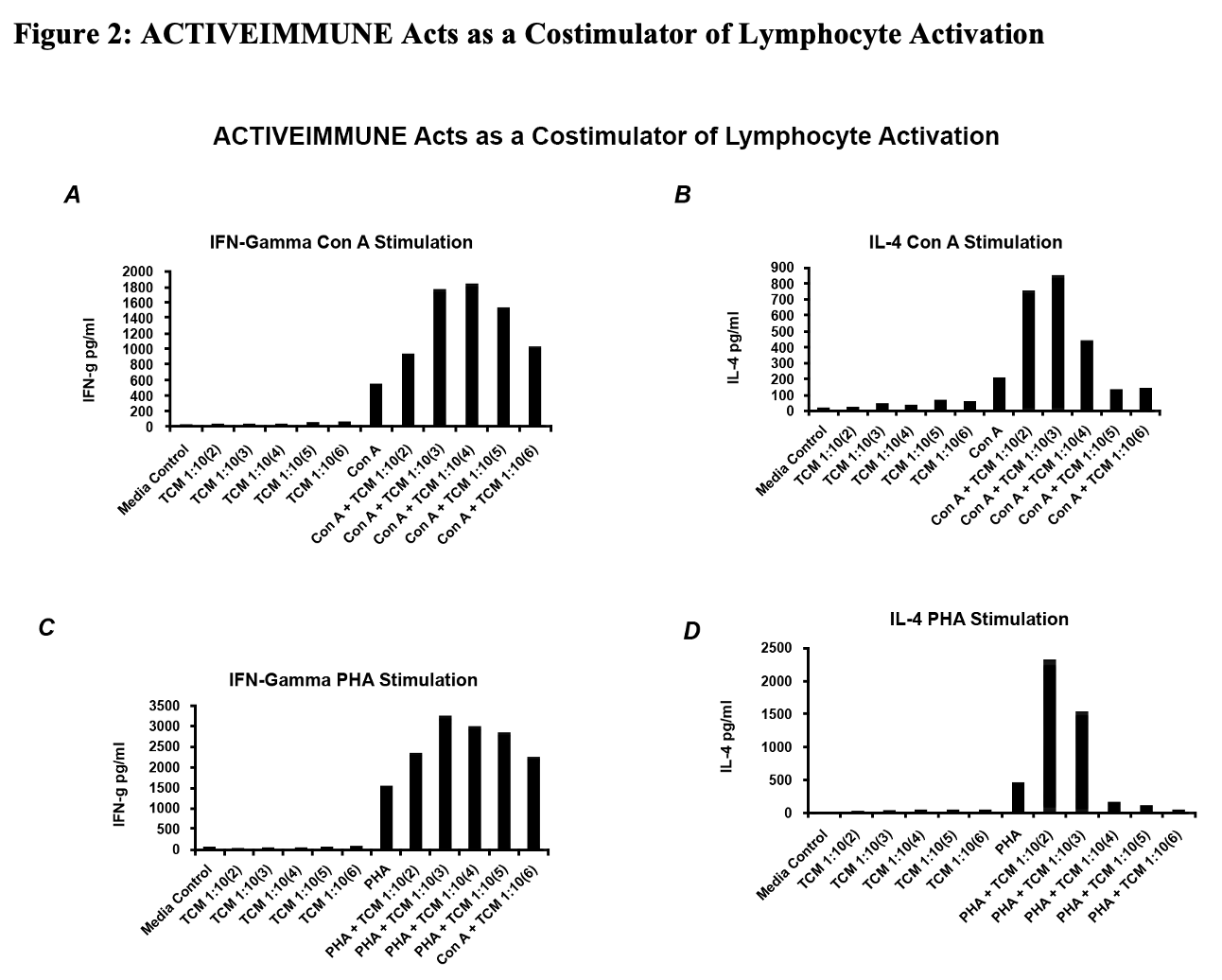
Given the contamination of
Figure 3:
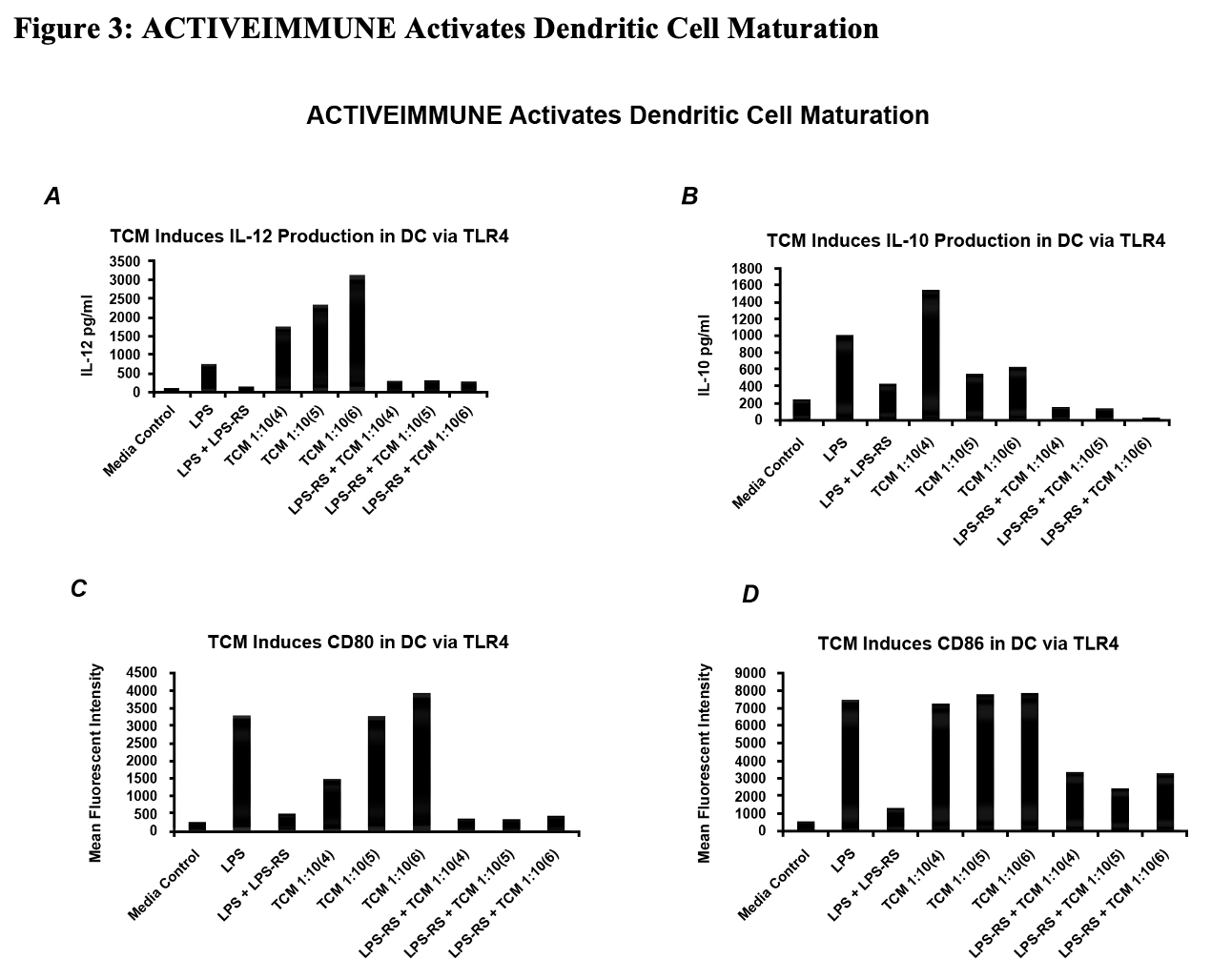
Molecular Characterization of
Two Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
Two-dimensional electrophoresis was performed according to the carrier
For the 10% acrylamide gels, after equilibration for 10 min in Buffer ‘O’ (10% glycerol, 50 mM dithiothreitol, 2.3% SDS
After equilibration for 15 min in Buffer “O” (10% glycerol, 50 mM dithiothreitol, 2.3% SDS
Figure 4: Gel Run of

Figure 4 illustrates the gel run under 10% conditions The arrowhead illustrates the molecular weight spot indicative of the immune modulatory activity that was subsequently sequenced.
Proteomic Analysis/Sequencing
Protein digestion and peptide extraction. Proteins that were separated by SDS-PAGE/2D-PAGE and stained by Coomassie dye were excised,
LC-MS/MS. The peptides mixture was analyzed by
Data processing and protein identification. The raw data were processed using ProteinLynx Global Server (PLGS, version 2.4) software as previously described [160]. The following parameters were used: background subtraction of polynomial order 5 adaptive with a threshold of 30%, two smoothings with a window of three channels in Savitzky-Golay mode
EFDVILKAAGANKVAVIKAVRGATGLGLKEAKDLVESAPAALKEGVSKDDAEALKKALEEAGAEVEVK
Mouse dendritic cells were generated by
Figure 6 Suppression of Tumor Growth by Leukocyte Extract Treated Dendritic Cells
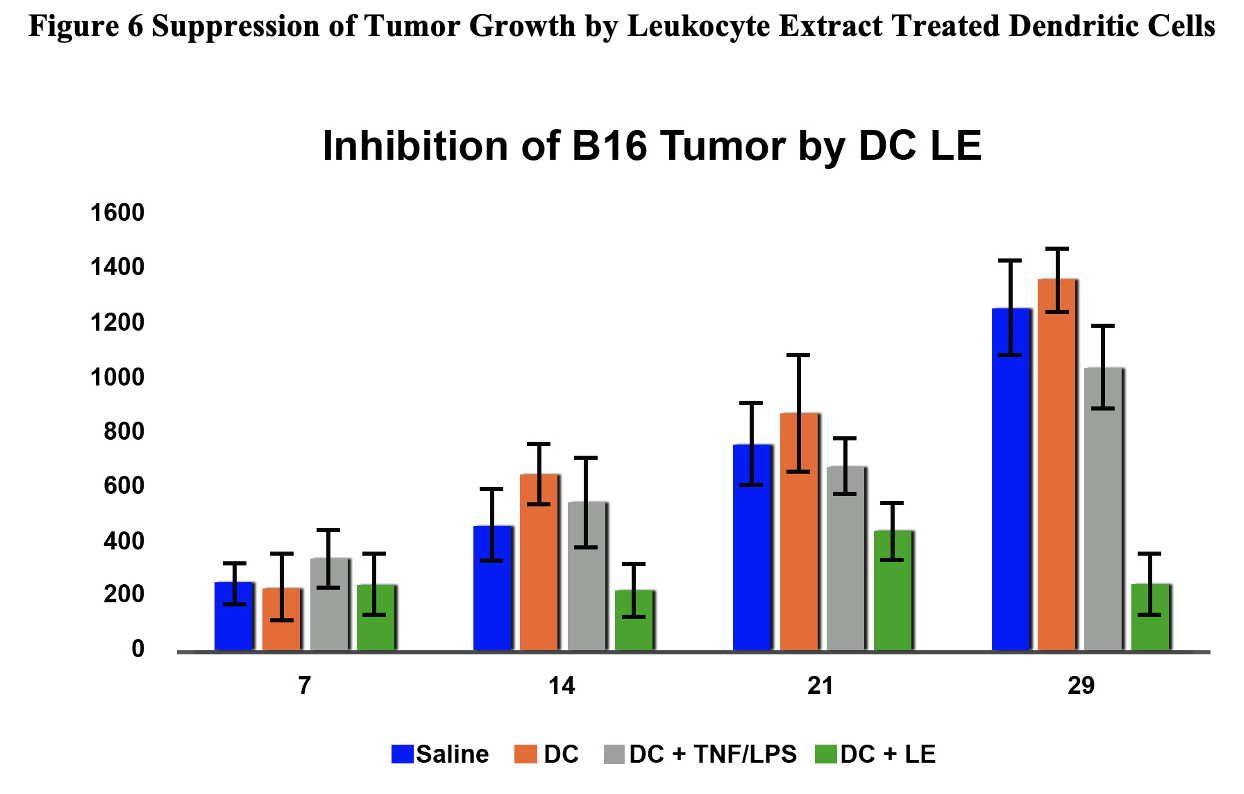
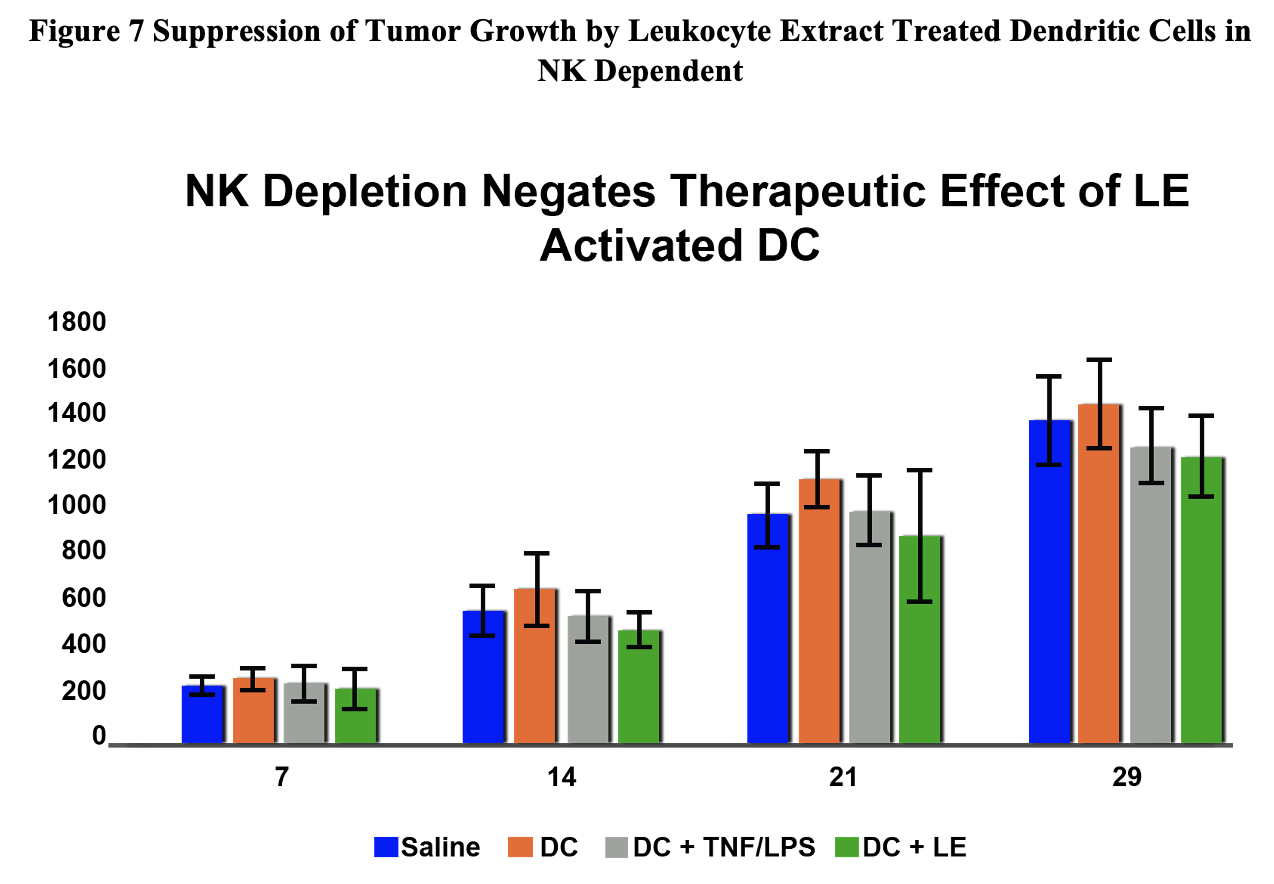
Figure 7 Suppression of Tumor Growth by Leukocyte Extract Treated Dendritic Cells in NK Dependent
StemVacs-L [Preclinical Done]
Augmentation of Natural Killer Cell Activity and Induction of Cytotoxic Immunity Using Leukocyte Lysate Activated Allogeneic Dendritic Cells: StemVacs™
Application No.: 63/045863
Stimulation of immunity would be beneficial in various chronic conditions such as viral infections and neoplasia. Autologous dendritic cell therapy has been widely described in the immunotherapy literature and has been approved by the FDA for treatment of prostate cancer. Unfortunately, the need to generate individual doses is costly and limited by ability of the patients to have sufficient starting cell numbers available to generate sufficient dendritic cells. Here we describe the process of preparing allogeneic dendritic cells utilizing a leukocyte lysate based approach. These data support development of StemVacs for conditions that would benefit from NK activation such as cancer and COVID-19.
StemVacs-H [Preclinical Done]
STIMULATION OF DENDRITIC CELL ACTIVITY BY HOMOTAURINE AND ANALOGUES THEREOF
Publication number: 20220235325
Abstract: Disclosed
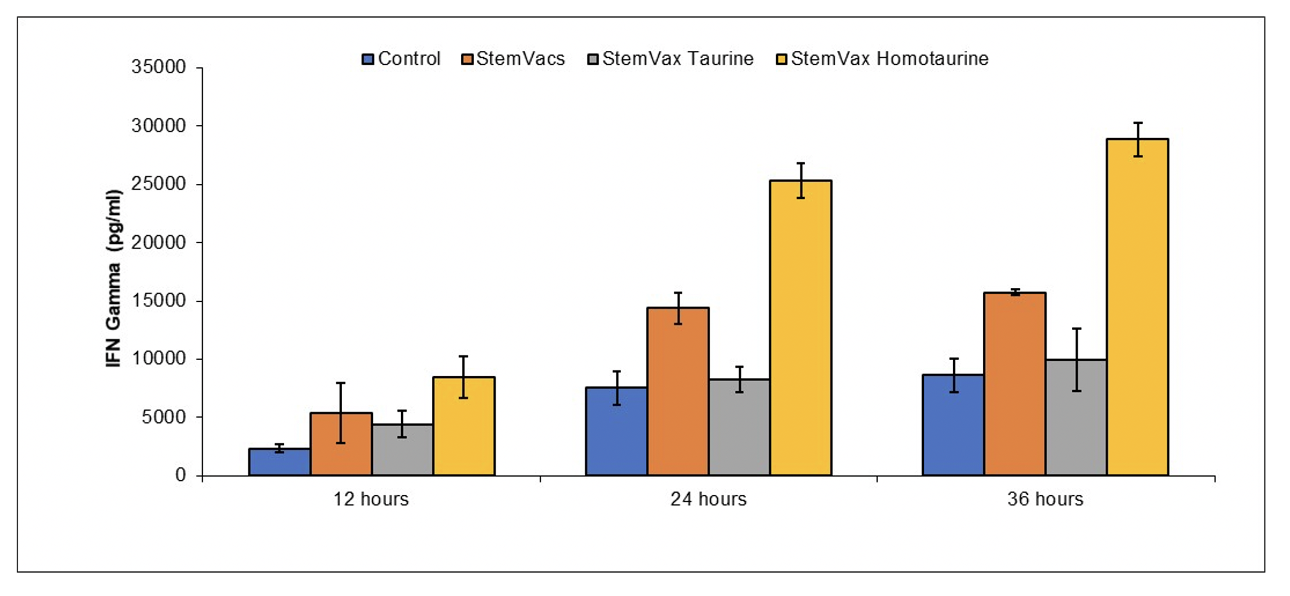
Example 1 Homotaurine Increases Ability of StemVacs to Stimulate NK Activity
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were obtained by
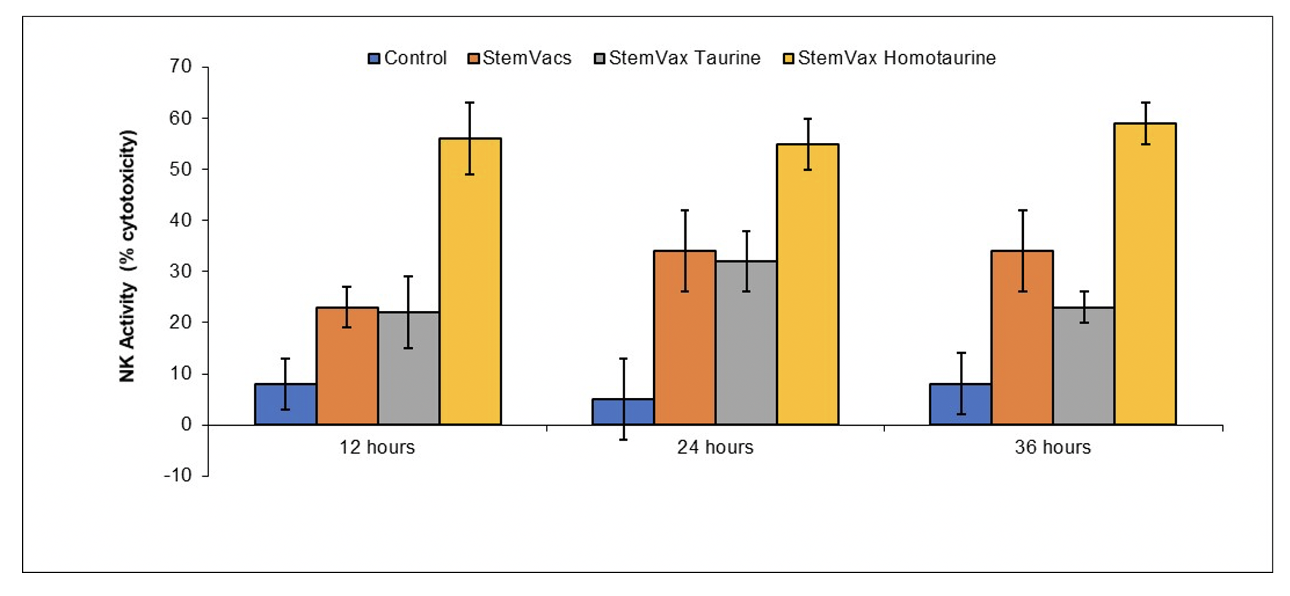
Example 2 Homotaurine Increases Ability of StemVacs to Stimulate T cell Activity
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were obtained by
JadiCell_DC_Exosomes [Preclinical Done]
Stimulation of Pulmonary Regenerative Exosomes by Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Derivatives Thereof
Application No.: 63/412861
Disclosed are therapeutic means for pulmonary degenerative conditions through the administration of mesenchymal stem cells in order to induce regenerative exosomes from dendritic cells expressing CD103. In one embodiment cultures of mesenchymal stem cells with dendritic cell progenitors are disclosed wherein said mesenchymal stem cells induce a modulation of STAT3 signaling in said dendritic cell endowing a regenerative property to said dendritic cells and exosomes derived from said cells.
JadiCell Delta Variant [Preclinical Done]
ENHANCEMENT OF UMBILICAL CORD MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY BY STIMULATORS OF T REGULATORY CELLS AND/OR CELLS EXPRESSING CD73
Publication number: 20230057356
Abstract: Disclosed
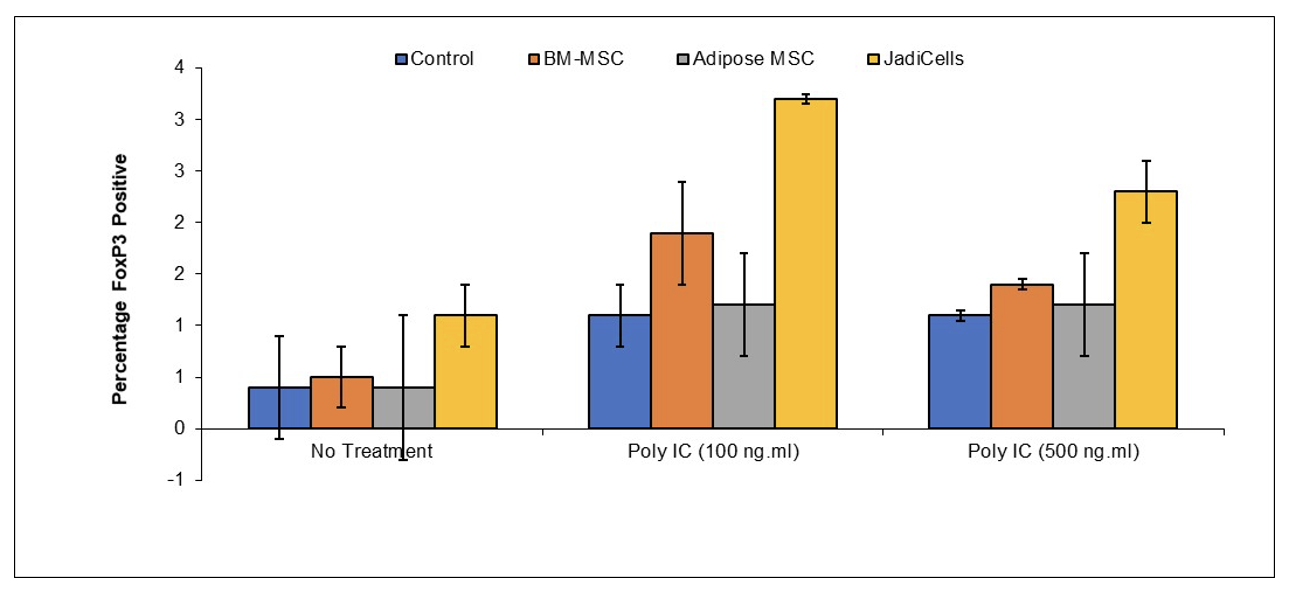
Example 1: JadiCells Increase the Number of T regulatory Cells
BALB/c mice were administered with 1 million of either bone marrow or adipose MSC or with JadiCells Intravenously at the same time as intraperitoneal injection of poly IC at the indicated concentrations. After a period of 3
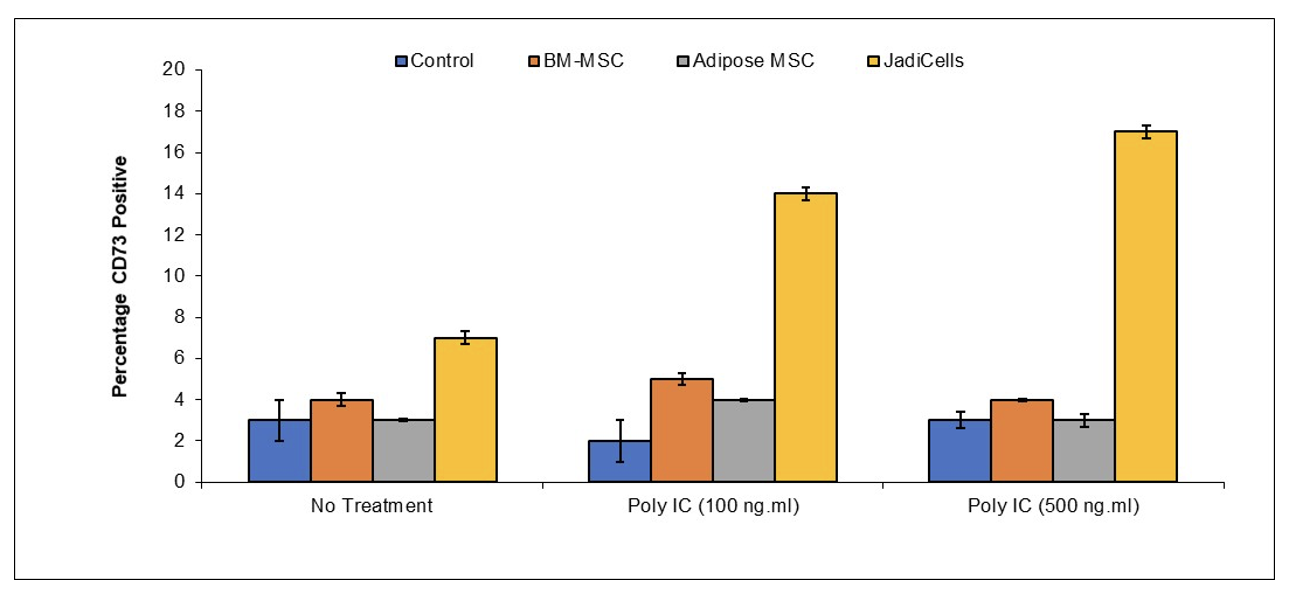
Example 2: JadiCells Increase the Number of CD73 T Cells
BALB/c mice were administered with 1 million of either bone marrow or adipose MSC or with JadiCells Intravenously at the same time as intraperitoneal injection of poly IC at the indicated concentrations. After a period of 3
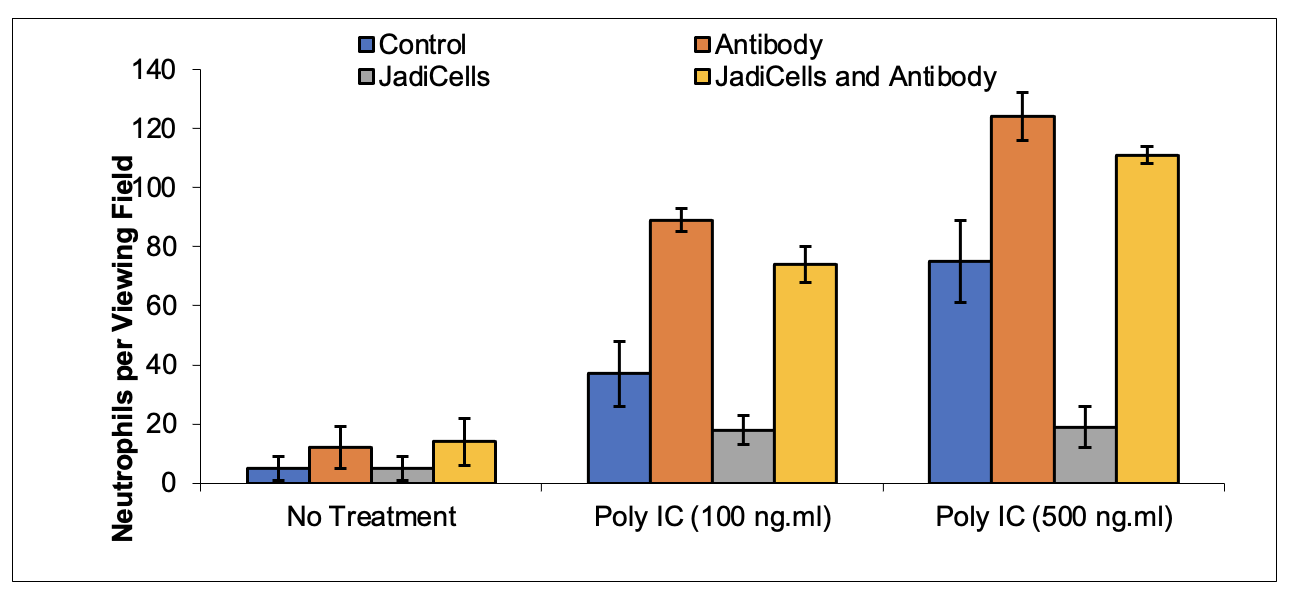
Example 3: Depletion of Treg Cells Decreases Therapeutic Potential of JadiCells
BALB/c mice were depleted of CD25 T regulatory cells by administration once every two days of anti-CD25 antibody one week before initiation of
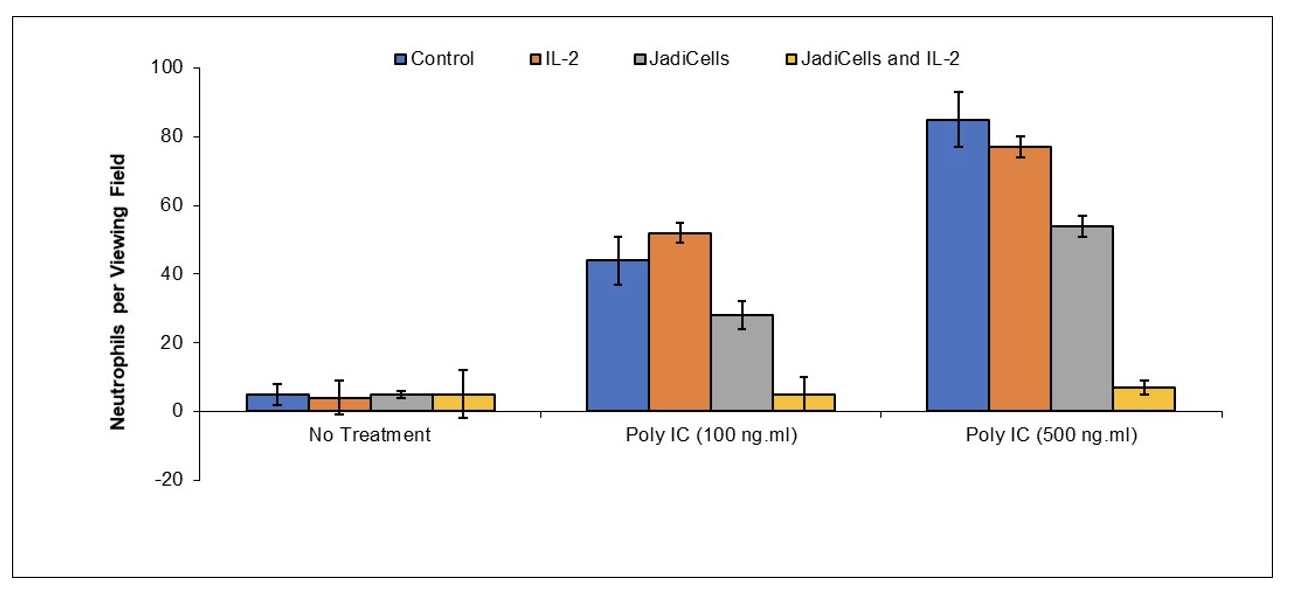
Example 4: Low Dose IL-2 Increases Therapeutic Potential of JadiCells
BALB/c mice were treated with IL-2 (10 IU/mouse) once every two days one week before initiation of
JadiCell IL-2 [Preclinical Done]
Enhancement of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapeutic Activity by Stimulators of T Regulatory Cells and/or Cells Expressing CD73
Publication number: 20230057356
Abstract: Disclosed
Example 1: JadiCells Increase the Number of T regulatory Cells
BALB/c mice were administered with 1 million of either bone marrow or adipose MSC or with JadiCells Intravenously at the same time as intraperitoneal injection of poly IC at the indicated concentrations. After a period of 3

Example 2: JadiCells Increase the Number of CD73 T Cells
BALB/c mice were administered with 1 million of either bone marrow or adipose MSC or with JadiCells Intravenously at the same time as intraperitoneal injection of poly IC at the indicated concentrations. After a period of 3

Example 3: Depletion of Treg Cells Decreases Therapeutic Potential of JadiCells
BALB/c mice were depleted of CD25 T regulatory cells by administration once every two days of anti-CD25 antibody one week before initiation of

Example 4: Low Dose IL-2 Increases Therapeutic Potential of JadiCells
BALB/c mice were treated with IL-2 (10 IU/mouse) once every two days one week before initiation of

JadiCell Leukine [Preclinical Done]
Inhibition and Reversion of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) by Endothelial Cell Regeneration
Application No.: May 12, 2022
Disclosed are means, treatment methods, and compositions of matter useful for prevention and/or reversion of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In one embodiment the invention provides the administration of mesenchymal stem cells and exosome thereof as a means of augmenting endogenous endothelial regeneration and/or endothelial regeneration stimulated by exogenous means. In some embodiments the invention provides administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells together with autologous endothelial progenitor cells and/or mobilization of said autologous endothelial progenitor cells.
JadiCell Lithium [Preclinical Done]
Lithium as a Monotherapy and/or Stem Cell Adjuvant Therapy for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Publication number: 20220370561
Abstract: Disclosed
Example 1: Lithium Enhances Ability of JadiCells to Increase T regulatory Cell Numbers in Mice.

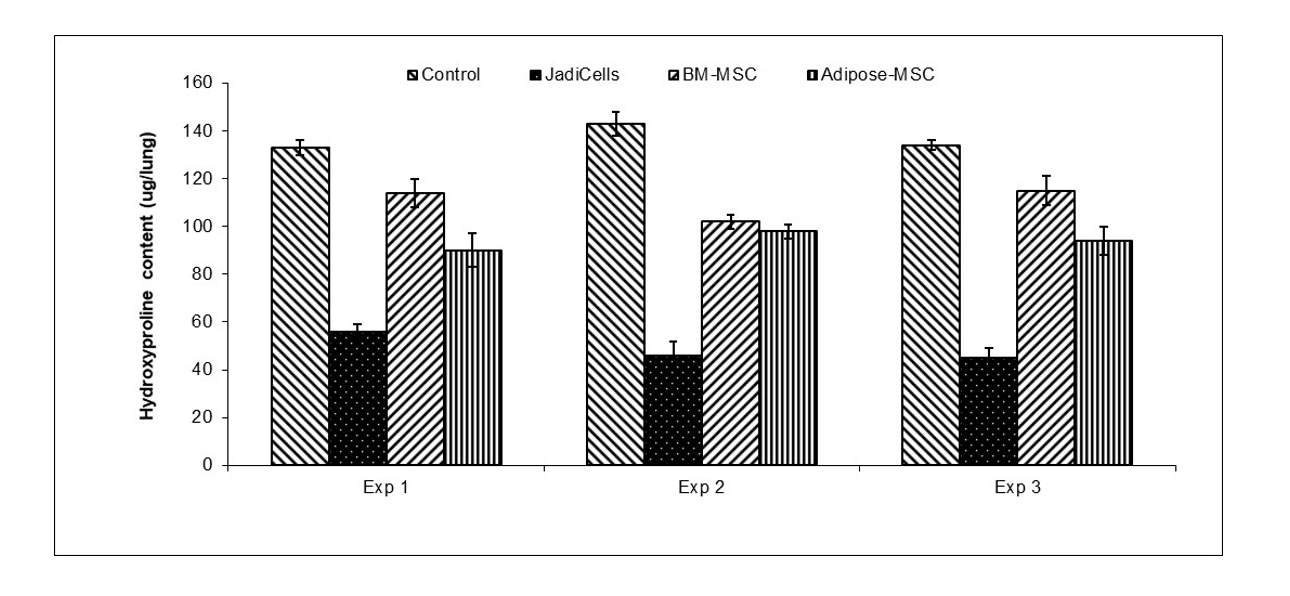
Example 2: JadiCells are Superior to BM and Adipose MSC
- Bleomycin (BLM)
administered intratracheally3 mg/kg in female10 week old C57/BL6 mice - JadiCell™ or BM-MSC or adipose administered by tail vein at 5 days after BLM
- Animals sacrificed at day 12 and assessed for fibrosis (hydroxyproline content)
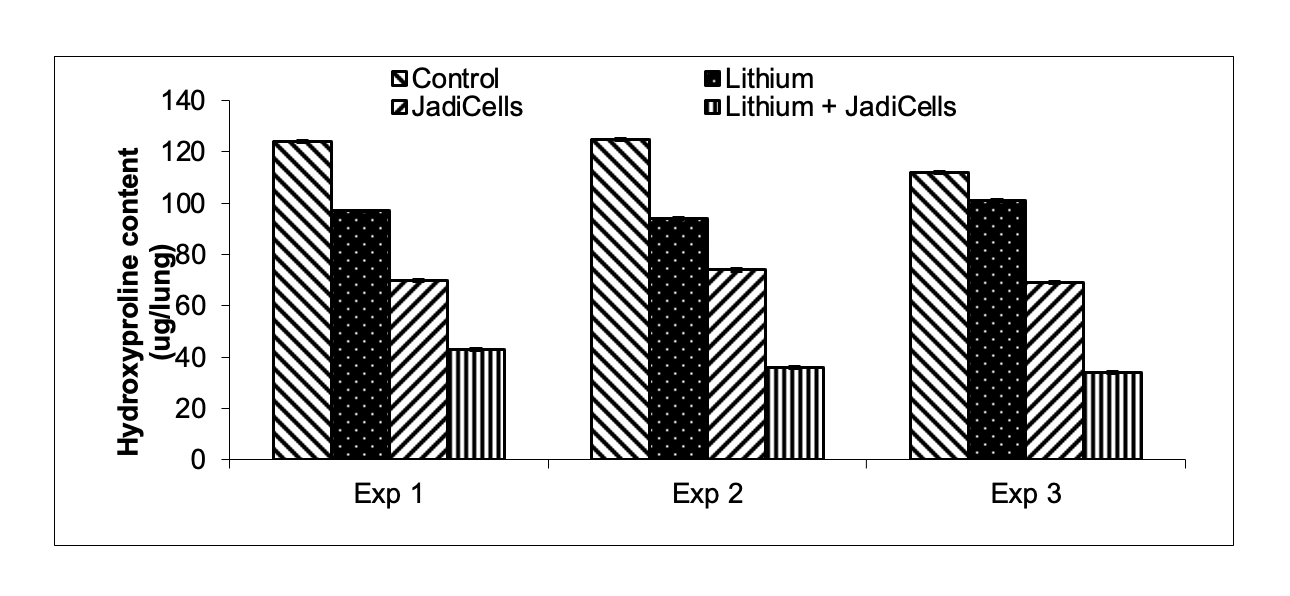
Example 3: Lithium Chloride Enhances Antifibrotic Activities of JadiCells
- Bleomycin (BLM)
administered intratracheally3 mg/kg in female10 week old C57/BL6 mice - JadiCell™ was
injectedby tail vein at 5 days after BLM. Lithium was injected IP as described in example 1.
Animals sacrificed at day 12 and assessed for fibrosis (hydroxyproline content)
JadiCell Neurogenesis [Preclinical Done]
Induction of Neurogenesis using Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Derivatives Thereof
Publication number: 20230047535
Abstract: Disclosed
Example
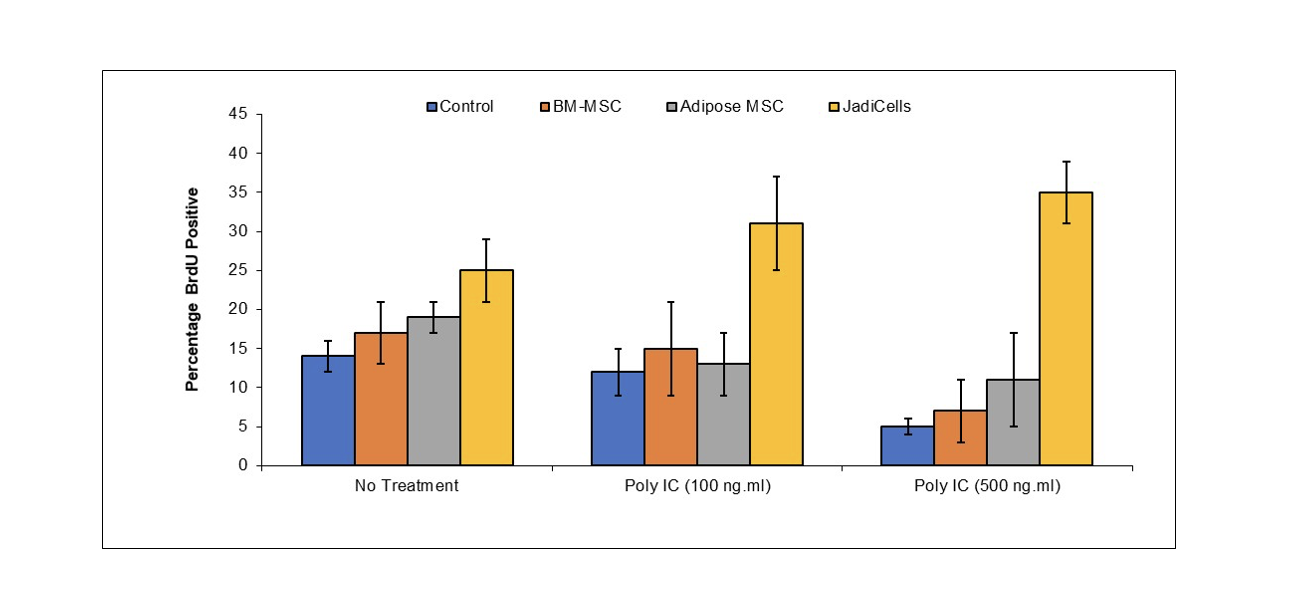
JadiCell Administration is Superior to other Stem Cells for Stimulating Dentate Gyrus Neurogenesis
BALB/c mice were administered with 1 million of either bone marrow or adipose MSC or with JadiCells Intravenously at the same time as intraperitoneal injection of poly IC at the indicated concentrations. After a period of 3
JadiCell T-regs [Preclinical Done]
Stimulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapeutic Activities by T Regulatory Cells
Application No.: 63/247016
Disclosed are novel means of enhancing mesenchymal stem cell regenerative activities including, intra alia, production from pulmonary leakage and suppression of scar tissue formation by co-administration with T regulatory cells. In some embodiments the invention provides an interaction between T regulatory cells and mesenchymal stem cells in which T regulatory cells stimulate upregulation of mesenchymal stem cell activity in a GITR dependent manner.
JadiCell Schizophrenia [Preclinical Done]
Immunotherapy of Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Associated Suicidal Ideation/Suicide
Application No.: 63/077723
Disclosed are methods, means, and protocols of modifying the immune system so as to induce an immunologically tolerant state insofar as T regulatory cell number and/or activity is augmented in a patient suffering from schizophrenia. In one embodiment T regulatory cells are administered to the patient from exogenous sources, be they allogeneic or autologous. In other embodiments, T regulatory cells are generated endogenously through administration of immature dendritic cells, mesenchymal stem cells, and/or pharmaceutical means.
TSOI-576 [Preclinical Done]
Induction of Concurrent Pulmonary Immune Modulation and Regeneration by Protein Mediated Conjugation of Immune Regulatory Cells with Endogenous Progenitor Cells
Application No.: 17/989588
Disclosed are means, methods and compositions of matter useful for treatment of inflammatory pulmonary diseases such as COVID-19 through administration of agents that facilitate interaction between immune modulatory cells and endogenous pulmonary progenitor cells. In one embodiment a bispecific antibody capable of facilitating the interaction between CD25 on T regulatory cells and CD47 on pulmonary epithelial stem cells is described.
Apoptocyte Cognition [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of Trauma Associated Cognitive Dysfunction Using Mesenchymal Stem Cell Apoptotic Bodies and Compositions Thereof
Application No.: 63/317505
Disclosed are means, treatments and compositions of matter useful for treatment of chemotherapy/radiotherapy associated cognitive dysfunction. In one embodiment the invention provides the administration of mesenchymal stem cell apoptotic bodies alone or in combination with “regenerative adjuvants” to prevent and/or reverse cognitive dysfunction associated with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. In other embodiments the invention teaches the utilization of stem cell apoptotic bodies for induction of neuroregeneration directly or indirectly.
Apoptocyte COPD [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Mesenchymal Stem Cell Apoptotic Bodies and Compositions Thereof
Application No.: 63/397503
Disclosed are means, treatments and compositions of matter useful for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In one embodiment the invention provides the administration of mesenchymal stem cell apoptotic bodies alone or in combination with “regenerative adjuvants” to prevent and/or reverse reduction in lung function associated with COPD. In other embodiments the invention teaches the utilization of stem cell apoptotic bodies for induction of pulmonary regeneration directly or indirectly.
innaMune [Preclinical Done]
Activated Leukocyte Extract for Repair of Innate Immunity in Cancer Patients
Application No.: 62/478498
Disclosed are compositions, methods of use, and pharmaceutical preparations useful for modulation of immune responses. In one embodiment a composition is extracted polyvalently activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells through dialysis. Said immune modulator is useful for treatment of cancer and alleviation of cancer associated immune depression. In one embodiment, said immunomodulator acts as a costimulatory of T cell activation by modulation of cytokine production. In one embodiment said immune modulator is concentrated for miRNA species capable of activating innate immune cells.
LymphoBoost [Preclinical Done]
Augmentation of Anti-Tumor Immunity by Mifepristone and Analogues Thereof
Application No.: 62/478507
The present invention relates to compositions of matter and methods useful for improving a treatment outcome and/or an alteration of immunity in a condition that benefits from immune stimulation. In particular, one embodiment of the invention teaches administration of sufficient doses of mifepristone or a derivative, alone, or in combination with an immunotherapeutic such as, but not limited to, an antibody, a vaccine, a cytokine, or a medicament whose therapeutic activity is associated with immune modulation.
MemoryMune [Preclinical Done]
Methods of Re-Activating Dormant Memory Cells with Anticancer Activity
Application No.: 62/478520
Disclosed are methods, protocols and compositions of matter useful for stimulation of anticancer immune responses. In one embodiment of the invention culture of buffy coat cells is performed in an environment resembling non-physiological conditions. Buffy coat derived products are subsequently harvested, concentrated, and added to a culture of monocytes and lymphocytes. Conditioned media from said second culture is subsequently utilized as an injectable solution for stimulation of anticancer immunity.
iPSC Chimera [Preclinical Done]
Pluripotent Stem
Publication number: 20220298491
Abstract: Disclosed
Example 1: iPS Derived Dendritic Cells Induce Reduction of B16 Melanoma
iPSCs (ATCC-DYR0100 Human Induced Pluripotent Stem (IPS) Cells (ATCC® ACS-1011™) were cultured on feeder layers of OP9 cells for 6 to 7 days in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FBS. The mesodermally differentiated cells were then harvested, reseeded onto fresh OP9 cell layers, and cultured in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FBS, 20 ng/mL GM-CSF, and 50 μmol/L 2-ME. On
Mice were inoculated with 500,000 B16 melanoma. Mice
iPSC Chimera/A-Gal [Preclinical Done]
Compositions Capable of Stimulating Immunity Towards Tumor Blood Vessels
Publication number: 20220403330
Abstract: Disclosed
Example
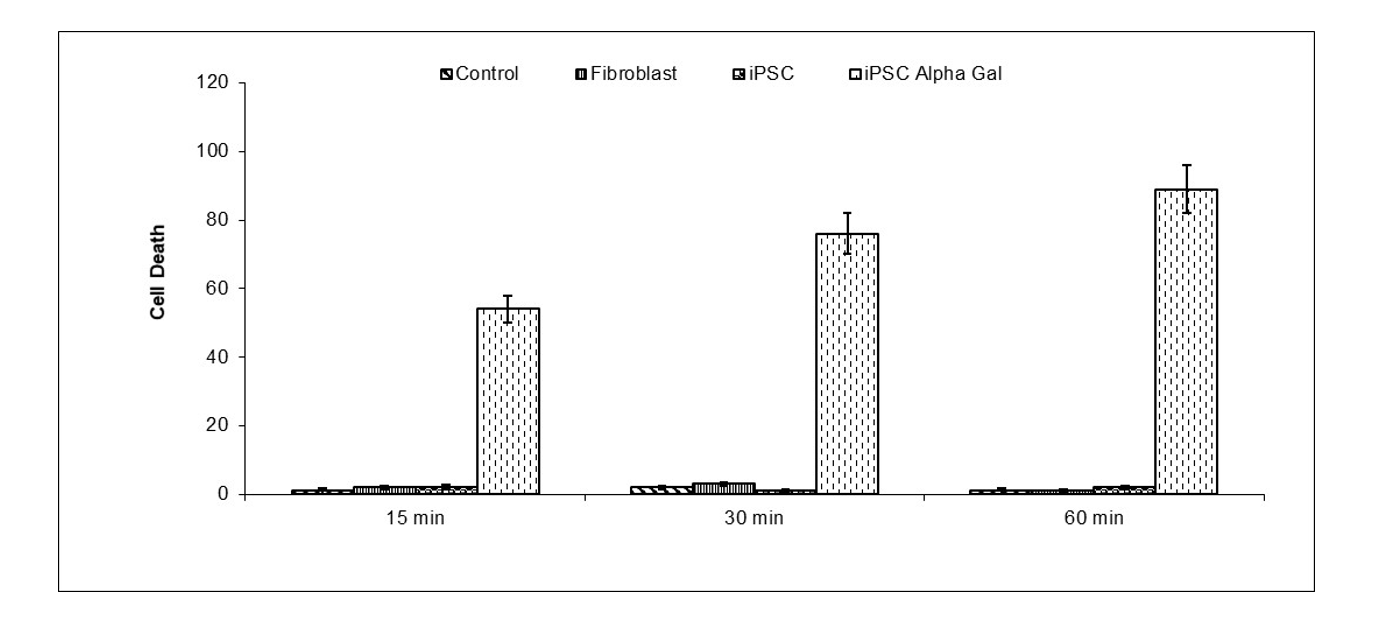
iPSC expressing α-Gal epitope (Galα1,3Galα1,4GlcNAc-R) were differentiated into tumor
NarcoStem [Preclinical Done]
Amelioration and Treatment of Opioid Addiction
Publication number: 20220323547
Abstract: Disclosed are compositions of matter, protocols
Example.
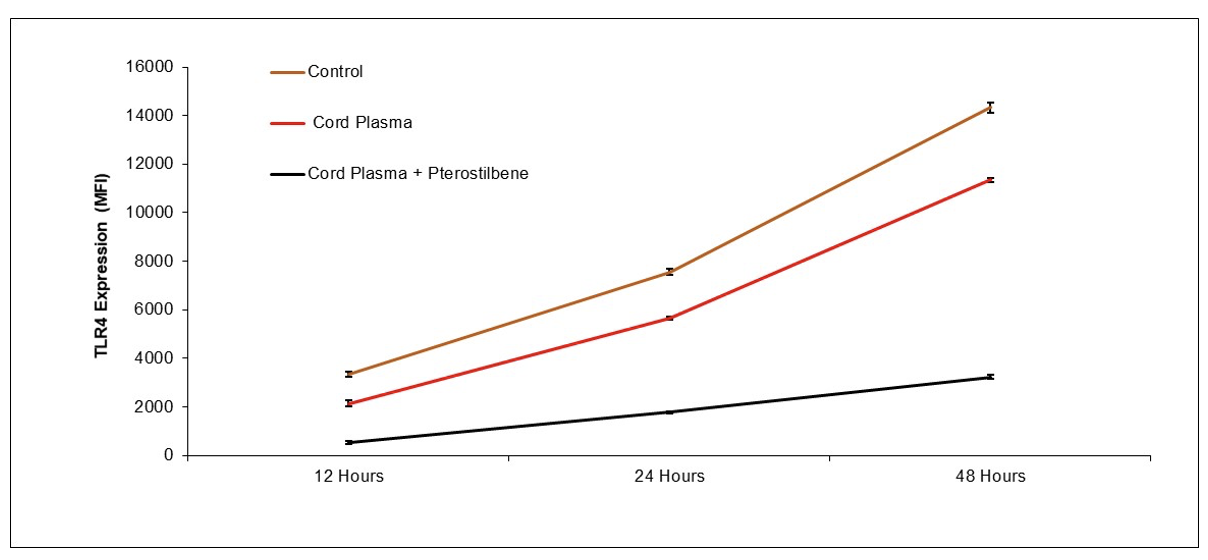
Neuroinflammation was induced by
NeuroLeukin [Preclinical Done]
Immunotherapy for Opioid Addiction
Publication number: 20220193127
Abstract: Disclosed
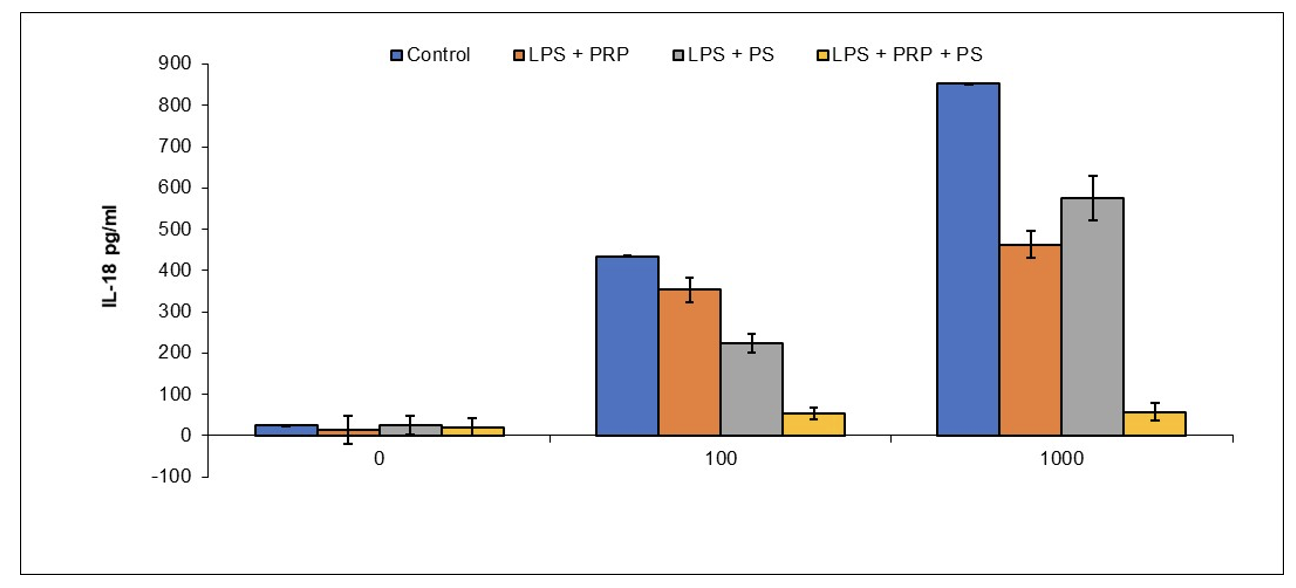
Example 1: Reduction of Brain Microglial Activation by PRP and Pterostilbene
BALB/c mice were anesthetized with isofluorane and administered
Example 2: Reduction of Brain Microglial Activation by PRP and Oxytocin
BALB/c mice were anesthetized with isofluorane and administered oxytocin (0.1 IU/mouse) and/or
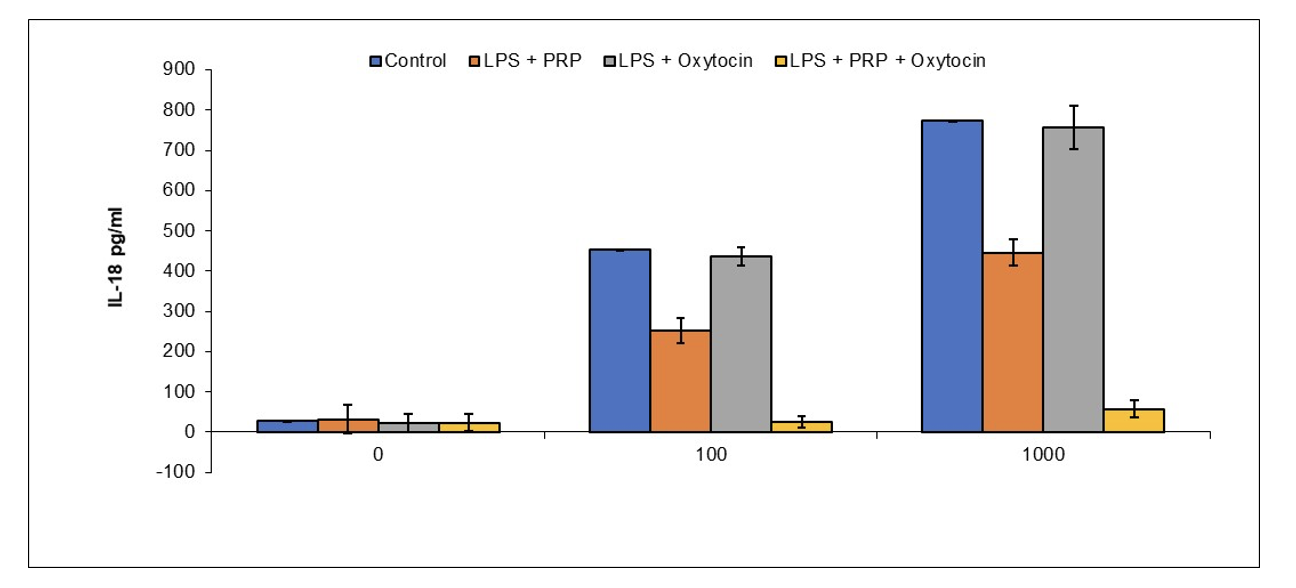
CampbellCell [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of Bipolar Disorder Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Modification of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Application No.: 63/408017
The invention discloses the utilization of mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells, conditioned media from mesenchymal stem cells, apoptotic bodies from mesenchymal stem cells, and modified mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of bipolar disorder. In one embodiment mesenchymal stem cells isolated from umbilical cord tissue are treated carbon monoxide at a concentration sufficient to induce activation of heme-oxygenase I and infused into a patient at risk or suffering from bipolar disorder.
siRNA ARDS [Preclinical Done]
Gene Silencing Therapy of Acute Respiratory Disorder
Application No.: 63/402304
Disclosed are treatment means, compositions of matter and protocols useful for suppression of acute respiratory disorder (ARDS) through induction of RNA interference in the pulmonary microenvironment alone and/or in conjunction with mucolytic and/or DNA disrupting agents. In one embodiment short interfering RNA (siRNA) is prepared which targets complement receptors C3R and/or C5R together with TNF-receptor, IL-6 receptor and/or TLR4 and TLR9. In some embodiments nanostilbene is utilized as a delivery vehicle for siRNA delivery.
RNA/CTE [Preclinical Done]
Treatment of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy via RNA Administration
Application No.: 62/775402
Disclosed are protocols, treatment means, and compositions of matter useful for treatment of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy through administration of RNA or modified RNA molecules. In one embodiment said RNA is generated to activate various toll like receptors (TLR), of which said activation leads to production of cytokines which paradoxically lead to protection from Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, wherein said protection constitutes a) reduction in glial cell activation, b) neuronal apoptosis due to excitotoxicity; and c) stimulation of endogenous regenerative processes including endothelial progenitor cell mobilization, proliferation of neuronal progenitor cells in the dentate gyrus and subventricular zones. In one particular embodiment targeting of RNA molecules is performed to specific brain cells including pyramidal neurons through the use of liposomes, exosomes, apoptotic bodies, nanoparticles and shark or cameloid antibodies is disclosed.
VSX-001 [Preclinical Done]
VasoSome’s product VSX-001 is a proprietary nanoparticle derived from specialized stem cells that can be utilized in a “universal donor” manner, meaning it does not have to be matched with the donor. The product possesses numerous properties of stem cells, including inhibition of inflammation, suppression of damage to blood vessels, and ability to regenerate damaged tissue. Advantages of administering VSX-001 compared to stem cells include: a) VSX-001 is substantially smaller in size than stem cells, allowing for superior distribution; b) VSX-001 does not multiply, thus possessing a superior long-term safety profile; and c) VSX-001 can be manufactured more economically as compared to stem cells.
Aneurysm Treatment by Exosomes which provides means of inhibition and/or treating aneurysms and other degenerated blood vessels through administration of regenerative cell derived exosomes, and/or regenerative cell derived apoptotic bodies. In one particular embodiment vessel regeneration is increased through administration of stem cell exosomes/or stem cell apoptotic bodies. Other embodiments include regeneration of vessels prone to aneurysms, repairing aneurysms of vessels, or acceleration of endothelialization after stent placement. Provided within the invention are methods of rejuvenating properties of said vessels associated with physiological health, examples of which include appropriate production of anti-coagulating/clotting factors, control of angiogenesis, and appropriate revascularization of injured tissue.
